Hello coders!! In this article, we will learn about spectrogram and see how to implement them in Python language from scratch. So, what does it mean? It is a point by point magnitude of the Fourier transform of a segment of an audio signal. Now let us understand the python spectrogram in detail.
Key Points about Python Spectrogram:
- It is an image of the generated signal
- In Y-axis, we plot the time and in X-axis we plot the frequency
- The color of the spectrogram indicates the strength of the signal
- It explains the distribution of the strength of signal at different frequencies
Let us first understand in detail about audio and the various forms of signals
Audio Wave Representation of Spectrogram:
 An Audio Wave
An Audio WaveA waveform is a visual representation of an audio signal or soundwave. We can observe the change in amplitude with time. The different axes represent:
- X-axis : Time
- Y-axis : Amplitude
Different Types of Waveforms:
1) Sine Wave:
 Sine Wave
Sine Wave- It is an S-shaped wave
- It oscillates periodically
- Continuous wave
2) square wave:
 Square Wave
Square Wave- non-sinusoidal wave
- it is periodic
- instateneous transition between the two levels
3) Triangular Wave:
 Triangular Wave
Triangular Wave- non sinusoidal wave
- periodic in nature
- piecewise linear
- only odd harmonics
Step wise Implementation of Spectrogram in Python:
1)Importing all the Libraries in Python
import os import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import librosa import librosa.display import IPython.display as ipd
- os – provides a way of using Operating system in a portable way
- matplotlib.pyplot – a collection of functions that make matplotlib work like MATLAB
- librosa – used to do an analysis on any sort of audio
- IPython.display – to display a Python object in all frontends
2) loading the audio
audio_path = "../input/audio/audio/" audio = os.listdir(audio_path)
listdir() – it is used to return a list of the entries in the directory given by path
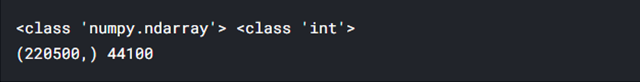
x, sr = librosa.load(audio_path+audio[2], sr=44100) print(type(x), type(sr)) print(x.shape, sr)
Let us visualize the waveform of the loaded audio in Python:
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5)) librosa.display.waveplot(x, sr=sr)
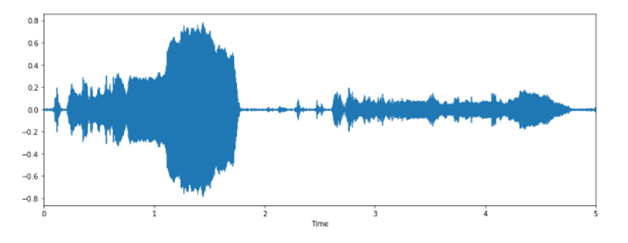 Audio Waveform
Audio Waveformlibrosa.display.waveplot() – Used to plot the amplitude envelope of a waveform
3) Converting the waveform to spectrogram in Python:
X = librosa.stft(x) Xdb = librosa.amplitude_to_db(abs(X)) plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5)) librosa.display.specshow(Xdb, sr=sr, x_axis='time', y_axis='hz') plt.colorbar()
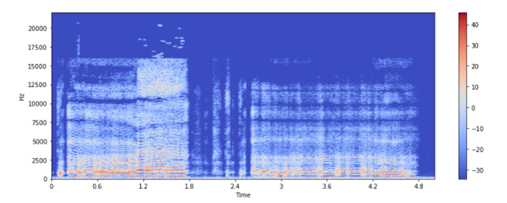
- librosa.stft() – STFT stands for Short-time Fourier transform .The STFT computes discrete Fourier transforms (DFT) over short overlapping windows to represent a signal in the time-frequency domain.
- librosa.display.specshow() – displays the spectrogram
Applications of PythonSpectrogram:
- Phonetically identify spoken words
- Analyse the calls of various animals
Must Read
- How to Calculate Square Root in Python
- Python Data Types | Mutable and Immutable Data Types
- Numpy Square Root | Usecase Evaluation of Math Toolkit
- Python Absolute Value | abs() Function With Examples
- Python Collections: Upgraded Version of Built-in Collections?
Conclusion:
In this article, we learned about spectrogram and their implementation in python. We also learned about different types of audio waveforms and saw how to convert the waveform into a spectrogram.
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
Happy Pythoning!
The post Python Spectrogram Implementation in Python from scratch appeared first on Python Pool.
from Planet Python
via read more
No comments:
Post a Comment